Chapter
What is cbd?
CBD, short for cannabidiol, is one of the most prominent cannabinoids found in hemp, a cultivar of cannabis sativa bred to exhibit low THC levels.
You may have heard of cannabinoids in reference to the substance THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol. Cannabinoids themselves are a class of chemical compounds that act similar to neurotransmitters in living things. Both cannabinoids, THC, and CBD come from the same plant, and even begin their existence from the same precursor materials; however, their effects on the body are very different.
THC is a cannabinoid known to be psychoactive, creating the signature “high,” and has a wide variety of effects, both medicinal and otherwise.
While both THC and CBD grow on the resin glands (called trichomes) of plants within the cannabis family, they are present in vastly different amounts. “Hemp” is classified as plants bred to exhibit less than 0.3% THC. In contrast, medical and recreational cannabis plants contain a large amount of THC and various amounts of CBD, CBN, THVC and other cannabinoids.


HEMP: HIGH CBD, LOW THC
HEMP: High CBD, Low THC
Marijuana: High THC, Low CBD
For cannabis to be considered hemp, it must contain less than .3% THC.
Hemp has many industrial uses and can be used to make clothing, cooking oil, canvas, and many other items.

The
Endocannabinoid
System
CANNABINOIDS DON’T JUST EXIST IN THE CANNABIS PLANT THOUGH; THEY OCCUR NATURALLY WITHIN THE BODY AND THROUGHOUT NATURE AS WELL.
All vertebrates (and even some invertebrates) produce cannabinoids. These bodily cannabinoids are referred to as endocannabinoids (the prefix “endo” means “from within”). The cannabinoids that come from plants are classified as phytocannabinoids (phtyo- from plant).
Phytocannabinoids have a nearly identical physical structure to endocannabinoids, allowing them to interact with our internal system of chemical passageways that endocannabinoids use, the Endocannabinoid System or ECS.
Just like the nervous system and endocrine system, the endocannabinoid system operates as a network throughout the body to send and receive important messages for our wellbeing in a variety of areas, though especially in the realms of appetite, pain sensation, mood, and memory.
WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS?

To better understand homeostasis, let's look at how we sleep.
When someone hasn’t had enough sleep that state is called “exhaustion,” and when one is too stimulated or feels too much energy, “edgy,” or “amped.” Between these two states is a sort of ill-defined ideal medium, “rested.” Rested itself is best understood as the state perfectly in between the two extremes, a kind of neutral stability.
The ECS is the system that helps direct the body back towards that stable state. It directs the other systems to tell the brain things like, “you need to be tired now,” or “you’ve
WHY DOES HOMEOSTASIS MATTER?
When the body is sick, it requires two things that are often in the shortest supply in life: time and energy. In the extreme, homeostasis sustains our life, meaning it helps one to avoid illness and death. A homeostatic immune system can fight off a disease and infection. Homeostatic oxygen levels keep one from death. However, beyond simply sustaining, homeostasis greatly contributes to the quality of life.
It may seem obvious to state, but when one is rested or free of pain, they have the energy to the things they need to do and also want to do. It is a state of health that allows us to appreciate and enjoy the body, not just exist within it. It is a state of opportunity as much as health.
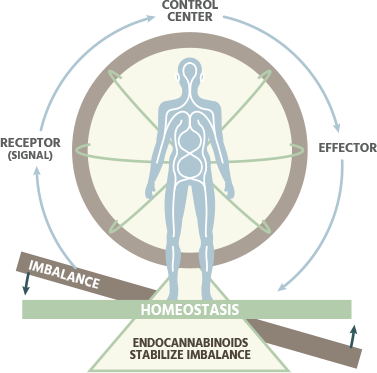

HOMEOSTASIS AND CBD
All supplementation, to some extent, is based on returning the body to homeostasis, a neutral state in which the body’s needs are balanced. Due to its similarity to endocannabinoids, CBD acts as a supplement to our natural transmitters and helps boost the essential processes being handled by the ECS to reach this state. CBD allows the ECS to function better and more efficiently, meaning one has more homeostasis, more resources to go out and live life. By being able to directly contribute to the vital state of homeostasis, many doctors and scientists believe cannabidiol has the potential to cause a paradigm shift in modern wellness.
Conclusion
- Exactly how CBD functions within the body is a complex process.
- Much like other areas of wellness, the unique mechanisms that make it work are still being studied and understood, however a growing body of research has revealed many of the mysteries inside us.
- Chapter 2 will explore CBD’s journey through the body in detail, and see how it supports the many vital systems driving our bodies every day.
Summary
- CBD is a non-psychoactive compound found in the hemp plant.
- CBD interacts with the body's endocannabinoid system.
- The endocannabinoid system is present in all of the body's major physiological systems
- The endocannabinoid system works to establish homeostasis in the body.
-
10






