CBD and Gut Health: How They Work Together
Sabina King on Jun 19th 2019
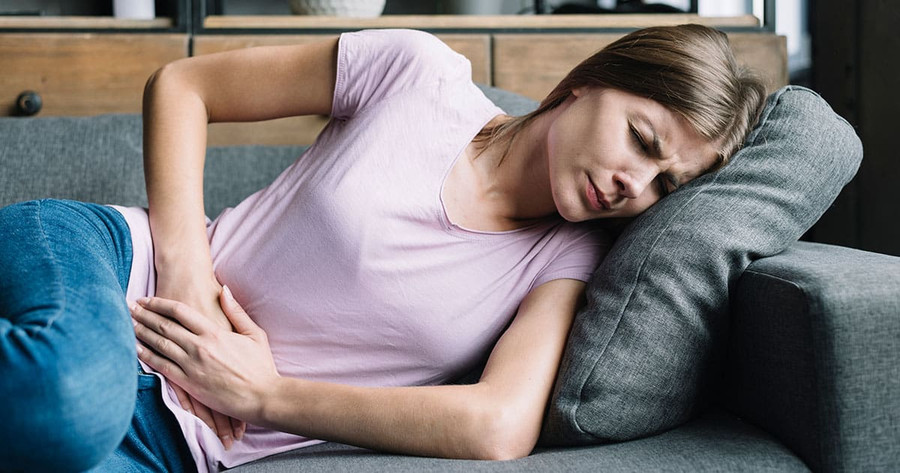
How does CBD improve gut health and promote healthy digestion? Research indicates that taking care of the gut is one of the most essential parts of achieving optimal health and wellness.
The gut is another word for your digestive system. It is responsible for absorbing nutrients from the food you eat. These nutrients support a wide range of function in the body including energy production, hormone balance, skin health, and mental health.
You may have wondered how the gut could be one the most important parts of human health and why so many people are taking probiotics. Is it just responsible for digestion, or does it do something more?
Key Facts About The Gut
Before we can understand CBD and gut health, it’s important to understand some key points:
 Around 70 percent of the immune system exists within the gut.1 By ensuring your gut is healthy, you’ll be saved from many different bodily woes because of the support your immune system receives.
Around 70 percent of the immune system exists within the gut.1 By ensuring your gut is healthy, you’ll be saved from many different bodily woes because of the support your immune system receives.
- Within the gut, there is a microbiome. Biome is a word that refers to any collection of plants or animals that exist within a specific location. The microbiome is the collection of both good and bacteria within the digestive system. It contains more than 10 trillion bacterial cells!
- There are tight junctions within the intestines that allow for nutrients to pass through into the bloodstream and prevent harmful microbes from leaving the intestines. When the microbiome is functioning properly and is full of good healthy bacteria, it prevents harmful substances from leaking into other parts of the body and causing harm.2
What does the microbiome do?
Digests fiber.
Healthy bacteria in the gut can help process fiber, which is then converted into compounds such as short-chain fatty acids.
Supports immune health.
Did you know that the microbiome can communicate with immune cells? It can support the body’s response to infection as well.
Maintains brain health.
The gut microbiome may also lead to the production of serotonin, an important neurotransmitter. The gut is connected to the brain through several nerves, which is why many researchers refer to it as the second brain.
What are the signs of poor gut health?
Frequently upset stomach.
Flatulence, diarrhea, bloating, acid reflux or constipation are the most obvious signs of poor gut health.
Inexplicable weight gain or loss.
An unhealthy gut will have trouble with the normal processing of nutrients and calories, leading to unintentional and seemingly random weight changes. Too much bacteria can lead to weight loss, while too little may lead to weight gain.
Constant tiredness.
As mentioned earlier, a lot of serotonin is produced in the gut, a lack of which has been tied to insomnia. This is turn leads to constant fatigue and sleepiness.
Food intolerances.
Food intolerances are different from allergies, which is when your immune system overreacts to a certain type of food. Intolerance refers to your digestive system having trouble digesting a certain food. Signs of this include nausea, gas, bloating or diarrhea in response to the trigger food. Research suggests that this may be due to a lack of good bacteria in the gut.
CBD and Gut Health
There are many ways in which CBD shows promise in promoting gut health.
Promotes the growth of good bacteria and restrains harmful bacteria.3 These good bacteria support the gut barrier while the bad bacteria can result in leakage and a weak intestinal barrier. By having more good bacteria in your gut, the entire health of your digestive system will improve.
CBD balances the endocannabinoid system. CBD works to promote health of the endoc
One study discovered that by giving a rat a probiotic, the number of endocannabinoids in the gut rose. Endocannabinoids are cannabinoids that are produced within the body. CBD is a cannabinoid. This study lead scientists to conclude that there must be a strong link between cannabinoids and probiotics and that the action of one may play a key role in the action of the other.annabinoid system. The endocannabinoid system is intertwined throughout the digestive system and the gut. It plays a role in supporting gut motility 4, aids in uptaking food, and encourages a healthy and regulated metabolism.5
CBD promotes overall digestive health. There are many different aspects of digestion that CBD can help with. One study found that CBD could promote a reduction in hyper-motility in mice.6Another found that CBD can help with many different types of gut discomfort including bloating and nausea.7
CBD strengthens gut barrier function.8 One study discovered that the body’s own endocannabinoids and phytocannabinoids like CBD show promise in not only preventing the damaging of intestinal lining, but also in repairing and promoting a healthy gut barrier. Disruption of the gut barrier has been linked to a multitude of different diseases.9
How You’ll Feel When The Gut Is Healthy

The gut plays a role in everything from mental health to your complexion. When you have a healthy gut, you may notice a few things:
- You’ll be in a great mood. The gut and the brain work together in a number of different ways. They can communicate directly through the vagus nerve. This nerve runs from the gut directly to the brain. The bacteria in your gut are also responsible for producing many of the different neurotransmitters that influence mood like oxytocin, serotonin, and dopamine. With a healthy gut, you’ll be in a great mood and be able to handle all the various stressors of life.
- Your skin will look beautiful. Over 70 years ago, scientists discovered that there was a link between the gut, the brain, and the skin.10 The gut has a major impact on hormones, and when the gut gets out of balance, hormonal levels can become imbalanced which can trigger damage to the skin. With a healthy gut, hormonal levels will be balanced, and you’ll experience beautiful glowing skin. CBD and gut health can both contribute to skin health.
- Your sleep will improve. CBD and gut health are both known to play a role in sleep. The gut has an effect on the hormones that determine your sleep cycle? When the gut gets out of balance, it can cause your circadian rhythm to become disrupted and making sleeping difficult.11 With a health gut, you’ll sleep better, which will have a dramatic impact on all aspects of your health.
- You’ll feel energetic and alive. Lack of energy impacts millions of people. A healthy gut and microbiome have a major impact on nutrient absorption and ensuring your blood sugar levels are optimal. By improving gut health, you can improve energy levels and overall mood.
Other ways to support your gut.
Eat different types of food.
A varied range of fibers, fruits and vegetables can support a happy gut.
Stock up on yogurt.
Fermented foods such as yogurt and sauerkraut contain strains of healthy bacteria.
Consume prebiotic fibers.
Prebiotic fibers are, in simple terms, food for the bacteria in your gut. Foods rich in prebiotic fiber include bananas, asparagus, oats and apples.
Take probiotics.
A lot of people choose to supplement a healthy diet with probiotics, which contain live bacteria that can support the gut.
Cut down on antibiotic use.
Antibiotics do not differentiate between good and bad bacteria and end up wiping the gut clean of healthy bacteria very often. It goes without saying that you should take antibiotics when medically necessary, but avoid overuse.
Conclusion
There are many different ways that CBD can promote a healthy gut. By promoting the growth of good bacteria, balancing the endocannabinoid system, promoting overall digestive health, and strengthening gut barrier function, CBD shows tremendous promise in improving the functioning of the gut.
When you have a healthy gut, many aspects of your life will change. You will experience a better overall mood, sleep better, have healthy skin, and experience greater energy levels and vitality. CBD is a recent discovery, and with time it is possible that even more benefits and links between CBD and the gut will be discovered.
Sources:
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2515351/ ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23201091 ).
- ( http://www.jimmunol.org/content/198/1_Supplement/219.20 ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4940133/#s002title ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21470818 ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27757083 ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27792038 ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21745190 ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4266989/ ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3038963/ ).
- ( https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22625848 ).